بص يا دكتور، خلينا نتكلم بصراحة … تحويل طقم كامل مؤقت (Interim Denture) لطقم نهائي على زرعات (Definitive Bar-Retained Overdenture) عملية دمها تقيل. ليه؟ لأنك مطلوب منك تنقل حاجتين في منتهى الأهمية وفي نفس الوقت:
-
وضع الزرعات بدقة ميكروسكوبية عشان تضمن الـ Passive Fit (وده روح الزرعات، لو مش موجود، المسمار يفك أو الزرعة يحصلها Bone Loss).
-
عضة المريض وشكل الأسنان (Occlusion & Esthetics) اللي ظبطناها في الطقم المؤقت والمريض اتعود عليها.
الطرق التقليدية بتاخد وقت ومواعيد كتير (Jigs، وتراي إن، وقصة طويلة). والديجيتال الكامل لسه فيه تحديات في نقل تفاصيل الأنسجة الطرية Soft tissues بدقة.
النهارده بقى جايبلك “الزتونة” من ورقة بحثية جديدة (Espona et al., 2026) بتقدم بروتوكول هجين (Hybrid) بيحل المعضلة دي بذكاء شديد.
1. الفكرة ببساطة: إيه هو الـ Hybrid Workflow ده؟
الفكرة قايمة على إننا نستخدم التكنولوجيا الديجيتال (Scanners & 3D Printing) عشان نعمل نسخة طبق الأصل من الطقم المؤقت، بس النسخة دي “مخصوصة” إنها تشتغل كـ Impression Tray وكـ Bite Registration في نفس الوقت.
يعني هنضرب عصفورين بحجر: هناخد مقاس الزرعات بدقة (Pick-up technique)، وهننقل العضة وشكل الأسنان في نفس الخطوة.
2. الخطوات العملية (Step-by-Step Protocol):
ركز معايا يا دكتور في الخطوات دي، لأن الترتيب هنا هو سر النجاح:
أ. تجهيز الطقم المؤقت (The Reference):
أول حاجة، لازم نتأكد إن الطقم المؤقت اللي مع المريض ده “مثالي”. العضة مظبوطة، والـ Vertical Dimension تمام، والشكل عاجب المريض.
-
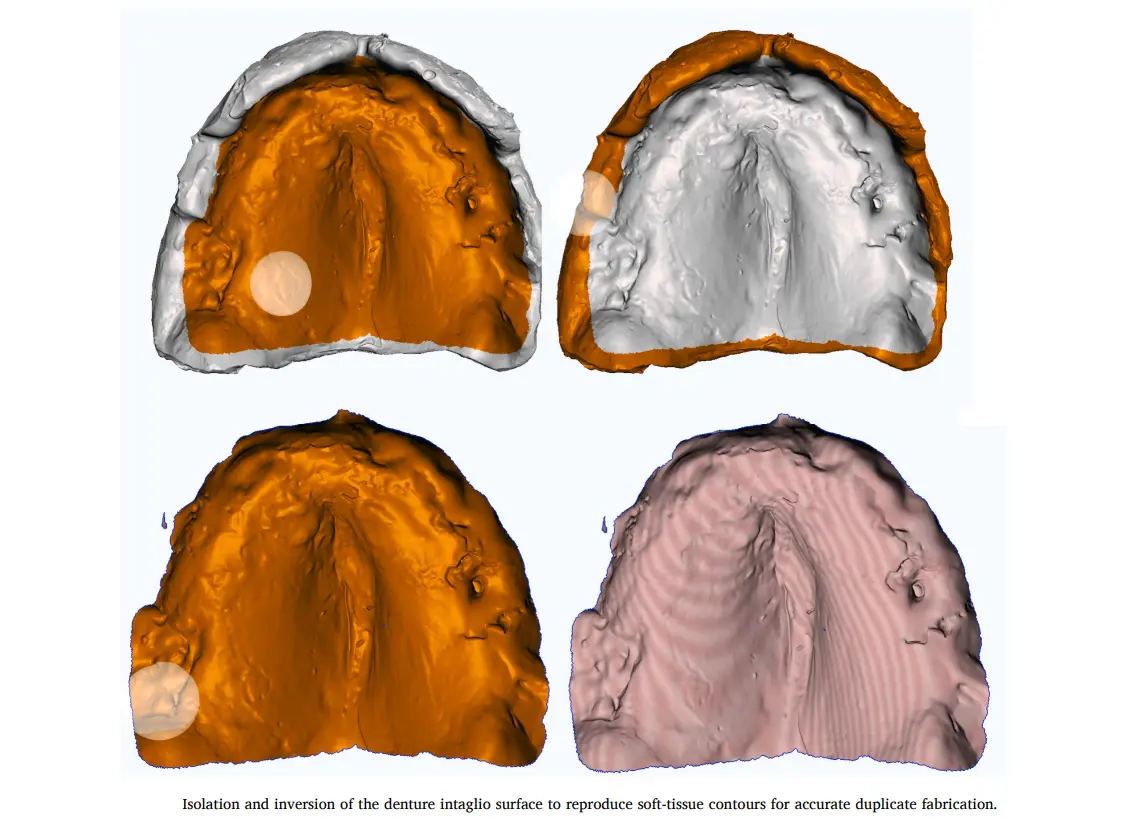
النقطة المهمة: بنعمل تبطين وظيفي (Functional Relining) للطقم ده باستخدام Light PVS عشان ننسخ شكل الأنسجة (Intaglio Surface) بدقة 100%.
ب. مرحلة المسح الضوئي (Scanning Strategy):
هنا بقى بيدخل دور الديجيتال. هنعمل مسح لحاجتين:
-
الطقم المبطن: بنعمله Extraoral Scan من بره ومن جوه (360 درجة).
-
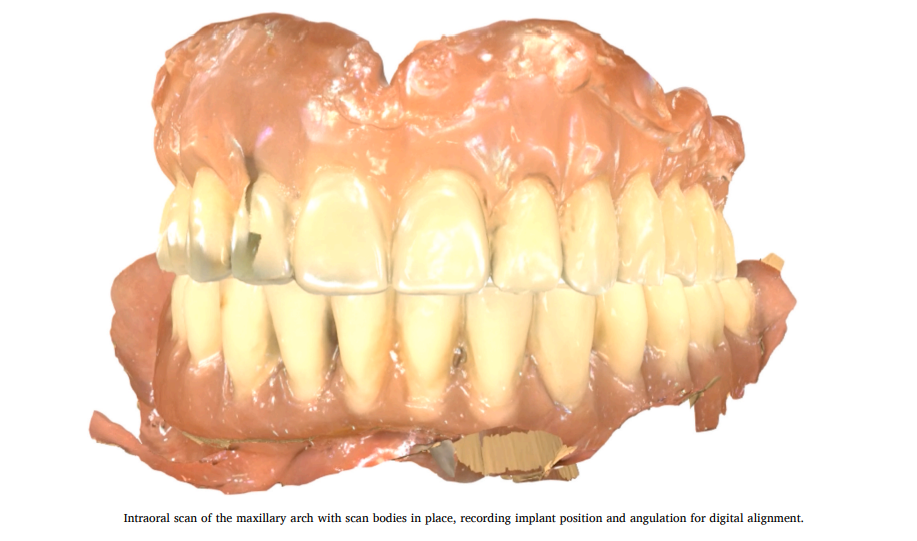
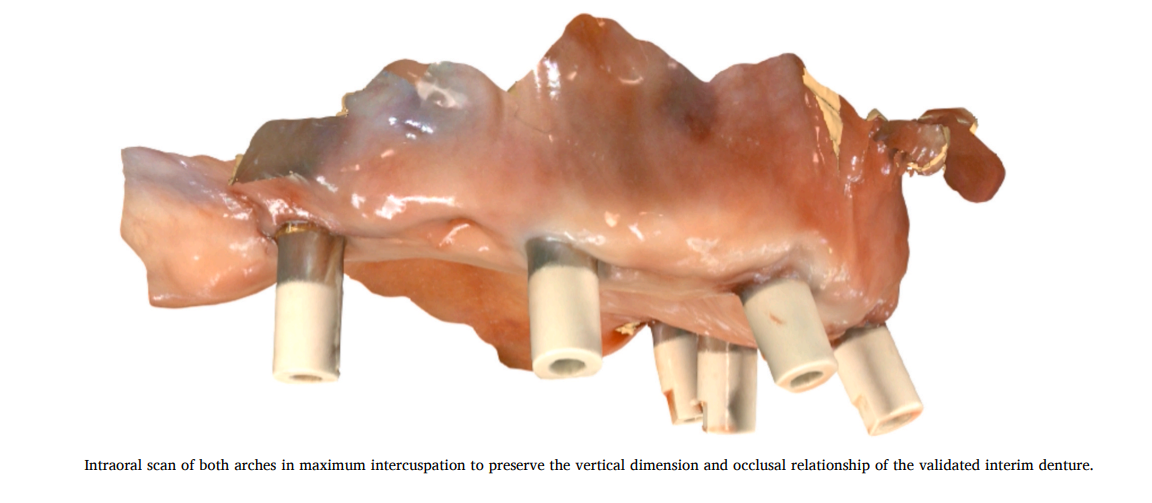
فم المريض: بنركب الـ Scan Bodies على الزرعات ونعمل Intraoral Scan.
(صورة الـ Intraoral scan للفك العلوي مع وجود الـ Scan bodies)
دي الخطوة اللي بنسجل فيها مكان الزرعات ديجيتال، لاحظ الـ Scan bodies واضحة إزاي.
ج. السحر في السوفت وير (Digital Alignment & Design):
هنا بقى “اللعب” كله. بنرفع الملفات دي على أي برنامج CAD (الباحثين استخدموا MeshMixer كحل مفتوح المصدر، بس ممكن تستخدم Exocad أو 3Shape).
-
بنعمل محاذاة (Alignment) بين سكان الفم وسكان الطقم. بنستخدم معالم الـ Palate (زي الـ Rugae) عشان نركبهم على بعض بدقة.
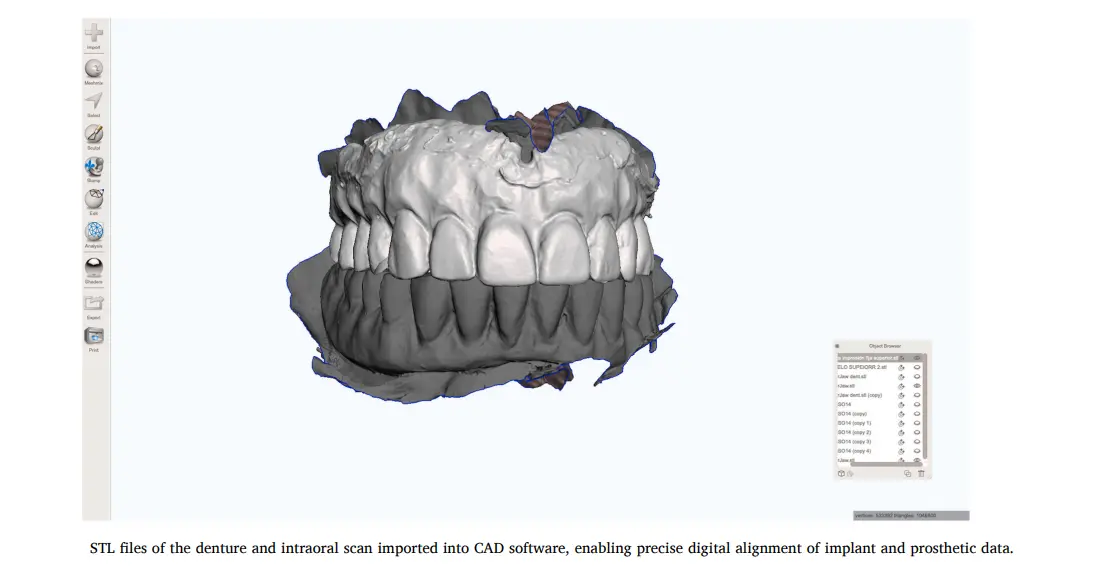
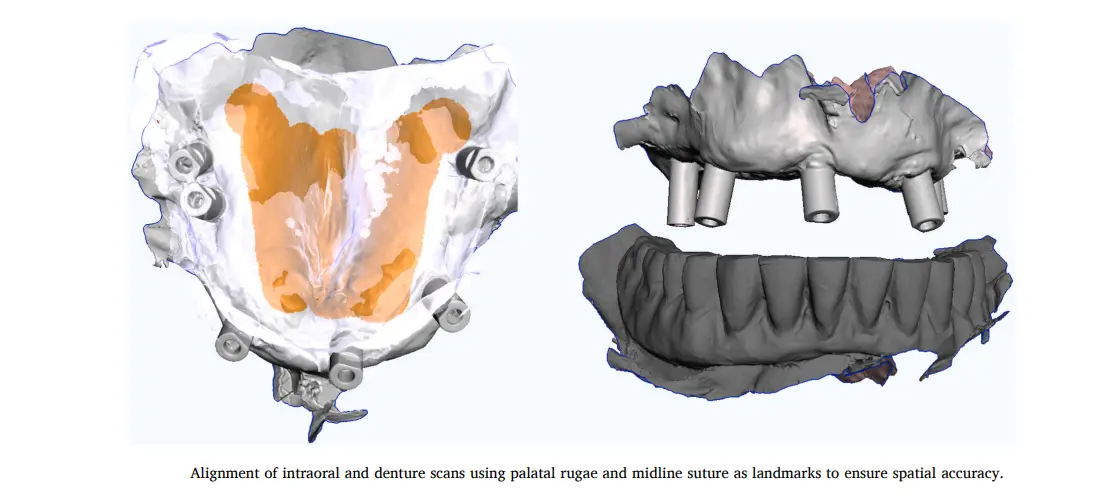
(صور توضح عملية الـ Alignment داخل السوفت وير)
لاحظ تطابق الـ Rugae Palatinae، ده اللي بيضمن إن الطقم الديجيتال راكب في مكانه الصح بالنسبة للزرعات. -
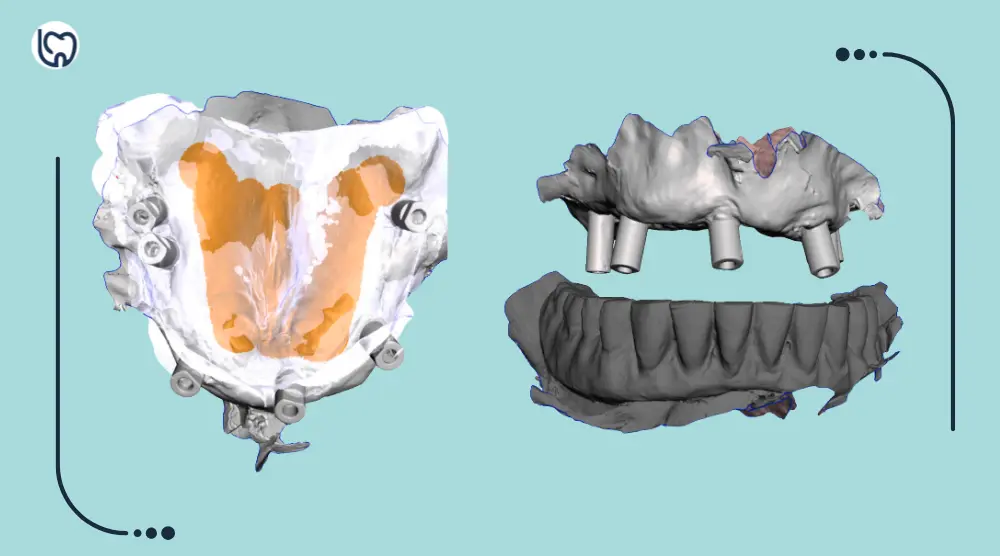
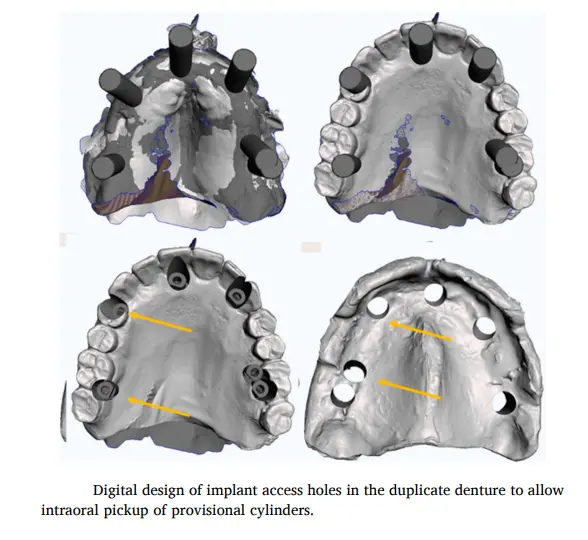
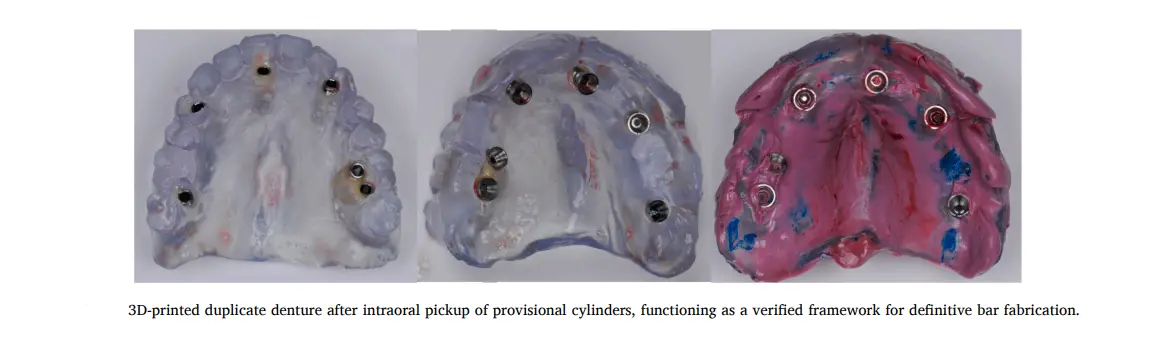
تصميم “التوأم” (The Duplicate): بنصمم نسخة من الطقم، بس بنعمل فيها “تركات” صغيرة:
-
بنعمل تفريغ مكان الزرعات عشان الـ Abutments تعدي مستريحة.
-
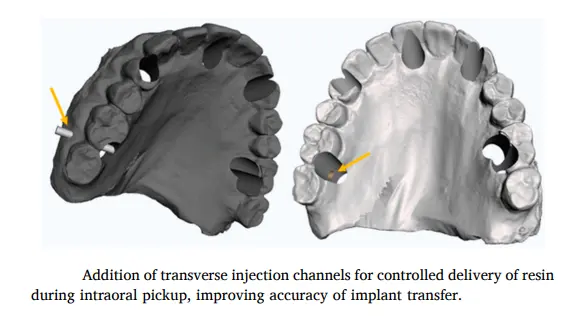
بنعمل قنوات حقن جانبية (Injection Channels). ليه؟ عشان نحقن منها المادة اللي هتمسك الـ Cylinder.
-
(صور توضح تصميم الفتحات وقنوات الحقن في السوفت وير)
القنوات دي هي السر اللي هيخلينا نحقن الـ Resin والمريض قافل بقه.
د. الطباعة والتجهيز (3D Printing):
بنطبع الطقم ده باستخدام Clear Biocompatible Resin. الشفافية هنا مهمة جداً عشان نشوف الـ seating بتاعنا كويس.
هـ. الخطوة الحاسمة: الـ Clinical Pick-up:
دي اللحظة اللي بنحول فيها الديجيتال لواقع ملموس (Analog):
-
نربط الـ Titanium Provisional Cylinders على الزرعات في فم المريض.
-
نلبس المريض الطقم المطبوع الشفاف (هيدخل مستريح لأننا مفرغين مكان الزرعات).
-
نخلي المريض يعض (Maximum Intercuspation). كده إحنا ضمنا العضة والـ VDO.
-
والمريض عاضض، نحقن Flowable Composite أو Resin من القنوات الجانبية اللي عملناها، عشان نربط الـ Cylinders بجسم الطقم.
-
بعد ما ينشف، بنفك المسامير ونطلع الطقم كله حتة واحدة.
(الطقم بعد ما طلع وفيه الـ Cylinders)
دلوقتي بقى معاك Jig نهائي، فيه مكان الزرعات بدقة (Passive Fit)، وفيه شكل الأسنان والعضة. ابعته للمعمل واطلب الـ Bar وأنت حاطط رجل على رجل.
3. ليه الطريقة دي “حركة معلم”؟ (The Advantages)
-
الدقة (Accuracy & Passive Fit): لأننا ربطنا الـ Cylinders جوه بق المريض (Intraoral Pick-up)، إحنا لغينا أي تشوه ممكن يحصل في الطباعة أو السكان. دي أدق طريقة معروفة لغاية دلوقتي.
-
توفير الوقت: العملية كلها خلصت في جلسة واحدة (حوالي 90 دقيقة). وفرت عليك وعلي المريض مشاوير رايح جاي.
-
راحة المريض: المريض مخرجش من عندك من غير سنان. الطقم المؤقت بتاعه لسه معاه سليم، وإحنا اشتغلنا بالنسخة المطبوعة.
-
التكلفة: مش محتاج معامل هاي-تيك غالية. أي طابعة 3D بسيطة وسوفت وير مجاني أو رخيص يقدر يعمل الشغل ده.
4. التحديات (Limitations & Takeaway)
عشان نكون أمناء علمياً زي ما اتفقنا:
-
الطريقة دي بتعتمد كلياً على إن الطقم المؤقت يكون مظبوط. لو الطقم المؤقت وحش، النسخة هتطلع وحشة (Garbage in, Garbage out).
-
محتاجة شوية مهارة في السوفت وير (CAD Skills) عشان تظبط الـ Alignment وتعمل الفتحات.
-
الورقة استخدمت MeshMixer، وده برنامج اتوقف دعمه، بس المبدأ واحد وممكن تطبقه بـ Exocad أو Blender for Dental.
الخلاصة يا دكتور
البروتوكول ده هو الحل السحري لحالات الـ Bar-Retained Overdenture. بدل ما تفصل خطوات المقاس عن خطوات العضة وتتوه بينهم، ادمجهم سوا.
استخدم الديجيتال عشان تعمل “Carrier” أو ناقل، واستخدم الأنالوج (Pick-up) عشان تضمن الدقة. هي دي “الصنعة” اللي بتفرق دكتور فاهم ومواكب، عن دكتور لسه شغال بالطرق القديمة المتعبة.
جرب الطريقة دي في حالتك الجاية، وابعتلنا!